How Much Money Do Food Companies Lose During An Hour Of Downtime
Downtime in manufacturing can wreak havoc on production standards. In fact, it is estimated that almost every manufactory loses at least 5% of productivity, with experiences as much as a twenty% loss, due to downtime. A manufacturer's lesser line can include upwardly to 800 hours of downtime which translates into millions of dollars in revenue loss. Minimizing downtime in manufacturing is just as pivotal as maximizing quality and output to maintain contribution margins. To understand the true cost of reanimation, you must rails and categorize every aspect of every bit well every bit analyzing the cost factors associated with each stop in production.
What is Downtime in Manufacturing?
Downtime in manufacturing is defined as whatever menstruation of time when a automobile is non in production. The full corporeality of downtime a factory experiences includes any stops during production that cause a loss of revenue for the company.
Reanimation in production is separated into two different categories: planned and unplanned. Planned downtimes are scheduled and budgeted stops during production such every bit scheduled maintenance and product changeover. Unplanned downtime in manufacturing occurs when equipment that is scheduled to be in operation has an unexpected event such
as equipment failures or running out of material occurs. Though all downtime has a toll, it is pivotal for manufacturers to service their machines as a form of prevention to decrease the chances of unplanned reanimation, a much costlier procedure.
Planned Downtime In Manufacturing
Scheduled machine maintenance is an example of planned downtime in manufacturing. Daily maintenance programs can include cleaning, lubricating parts, making pocket-sized adjustments and detecting minor problems that tin can be corrected before they become a major problem that can shut downwards a production line. Production changeover is another example of planned downtime. Production changeover is a process that occurs when a manufacturing institute switches from producing ane product to another during a planned downtime. A typical changeover consists of setup and adjustments such as ramping up and down both at the start and end of a run.
Planned downtime still has a cost to revenue, so the priority is to expedite motorcar maintenance and product changeover to remain within the budgeted timeframe. This isn't always the case and delays have an bear upon on the Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) every bit well as contribution margins.
Unplanned Downtime In Manufacturing?
Unplanned reanimation are whatsoever unexpected stops that occur during product. The stops occur without find and can concluding any length of fourth dimension and can create massive backups along the product line.
These unplanned halts during production eat into the maximized hours in a work day and inevitably diminish optimized revenue.
Many times, this can be due to hardware or process failures; for example, a pump, motor or fan could fail on a piece of equipment which would require unplanned machine maintenance. The time needed to ameliorate the failure is in direct correlation to the constraints of having the necessary materials to fix the hardware, too as having a knowledgeable workforce with the ability to address and resolve the result. The consequences of these unplanned stops are a loss in hourly production rates and are translated into a loss of revenue. For every moment a motorcar is non operating, acquirement is lost.
Auto Jams: An operator must be present to physically manipulate the component that is jammed on the automobile. If an operator is non nowadays on the factory floor, one must exist brought in, and reanimation is exacerbated past this look.
Part Failures: Auto downtime can be caused by office failures such as pumps, belts, sensors and motors that require replacement or repair. The length of downtime is determined by the availability of the materials necessary to brand the required repairs, and if a maintenance technician is bachelor to make those repairs.
Water & Oil Leaks: The size of a h2o or oil leak and the accessibility to the leak by an operator will affect the length of downtime. Containment of a leak to prevent damage to other machine components is also a constraint on how rapidly an operator tin can have the product line running efficiently once more.
Inadequate Maintenance: Unplanned downtime can effect when machines are non maintained or checked adequately during scheduled inspections. With inadequate maintenance, the probability of impairment and prolonged downtime not only increases simply creates an environment that is non safe for factory floor workers.

What Are The True Costs of Downtimes?
The True Costs of Downtime (also known equally TDC), consists of analyzing all cost factors associated with downtime. The two variables of TDC are tangible costs and intangible costs. This information is and so used for direction decisions and for the justification of costs.
Co-ordinate to the Vanson Bourne Research Study, roughly 82 pct of companies that take experienced unplanned downtime over the past three years, accept experienced outages that lasted an average of four hours. The cost of downtime came with a price tag of an estimated 2 million dollars. With noesis of these statistics, the priority for manufacturing companies is to accomplish maximum efficiency past eliminating unplanned downtimes altogether.
Tangible costs are the physical consequences of downtime in manufacturing and are recorded and tracked by data.
Lost Product: Every product that a manufacturer produces represents some amount of potential profit. Whether it'due south pennies or dollars, these values add upward over time-based on how fast each unit is produced. For example, allow'southward say a company can produce 100 units per minute, and each of these units represents a potential of $one of profit. For this company, the toll of reanimation in manufacturing based on lost production would be $100 per minute, $6000 per hour, etc.
Lost Capacity: When all systems are fully operational, a manufacturing constitute that is running at suboptimal capacity. Information technology is important for a factory to program for when at that place is a sudden increase in demand. When this occurs, the factory will need to operate at a higher chapters to fulfill the added business. Reducing production reanimation is important because it creates boosted capacity for free and makes situations similar these a not-event.
Direct Labor: When you reduce reanimation in manufacturing, your production levels go up while your labor stays the same. This volition decrease the labor cost per unit . Besides, when there are less issues, employees can focus on their main task and increment their efficiency.
Inventory: The cost of holding inventory is typically around x%-thirty% of the inventory's value, per year. This means that if you take 1 1000000 dollars of inventory, it would cost $100,000 to concur information technology for a yr. 1 cause of reanimation is changeover betwixt products. Reduced changeover reanimation will let smaller lot sizes and lower inventory levels, which will lead to a lower toll of holding.
Intangible Costs Are Less Obvious, Focus On Factory Personnel
The intangible toll of reanimation in manufacturing is less obvious because information technology is less concrete. Many of these costs are focused on the relationship of a workforce within a sure environs and how humans and machines interoperate.
Responsiveness : When downtime occurs, employees must focus on addressing these issues equally their top priority. Since the cost of downtime in manufacturing is so meaning, information technology becomes more important to solve these problems than focusing on customer service bug. For case, the TDC in the automotive industry is around $22,000 per minute!
Stress : Downtime can cause a lot of stress in both employees and the machines that they are operating. When a system isn't working, it tin can get overwhelming for an employee to reach their daily tasks. On the other hand, if a automobile needs to produce at their maximum capacity for long periods of time, it becomes more likely that they will malfunction. People and machines perform better under less stress.
Innovation : Downtime can exist a very fourth dimension-consuming issue for a business. This takes away fourth dimension from other things similar innovation and creative brainstorming opportunities. It is much more important to make certain a electric current system is working before imagining how to improve that organisation'southward capabilities for the hereafter.
Calculating The True Cost of Downtime
The true cost of downtime in manufacturing is determined past the bear on an outage will have on employees and productivity. By identifying the cost of employee downtime equally well as the cost of loss of orders, manufacturers can calculate a concrete number the truthful cost of unplanned downtime.
To decide the cost of employee downtime, start calculate the average hourly pay rate of impacted employees. 2d, assign a per centum for the level of impact that unplanned downtime will have on productivity. For example, if merely xxx% of the product line is operational, the loss in productivity equals seventy%. If you have 150 employees at an hourly rate of $50 and they experienced a 70% productivity rate loss, the full toll of employee downtime would be $v,250.
The cost of impacted employees from unplanned downtime directly correlates to a decline in product being manufactured, leading to a loss in orders. The overall toll is as well compounded by the inability to produce. To calculate this loss, calculate the production hours per day, the average amount of units produced and the hours of unplanned downtime. Dividing the average units produced by the hours of unhalted production during a solar day. For example, $300,000 in sales orders over the grade of an eight-hr shift amounts to $37,500 in sales orders created per hour. Multiply this acquirement by the total hours of unplanned downtime volition reveal that $150,000 is the total price of unplanned downtime.
Why Is Knowing The Cost Of Downtime Important?
There are many reasons why understanding downtime costs is important to optimizing day to solar day operations throughout production. For case, if you are enlightened that a half dozen-hour outage for a major repair will toll $500,000, you will take preventative measures to avert this outage equally smaller scheduled repairs that consist of xx-30 infinitesimal stops and have a much smaller cost tag.
Past understanding the importance of downtime costs manufacturers can make data-driven decisions with conviction. Operations teams can avoid unnecessary costs and extensive planning and preventative deportment can be taken to avoid meaning amounts of unplanned downtime.
How To Reduce Reanimation In Manufacturing
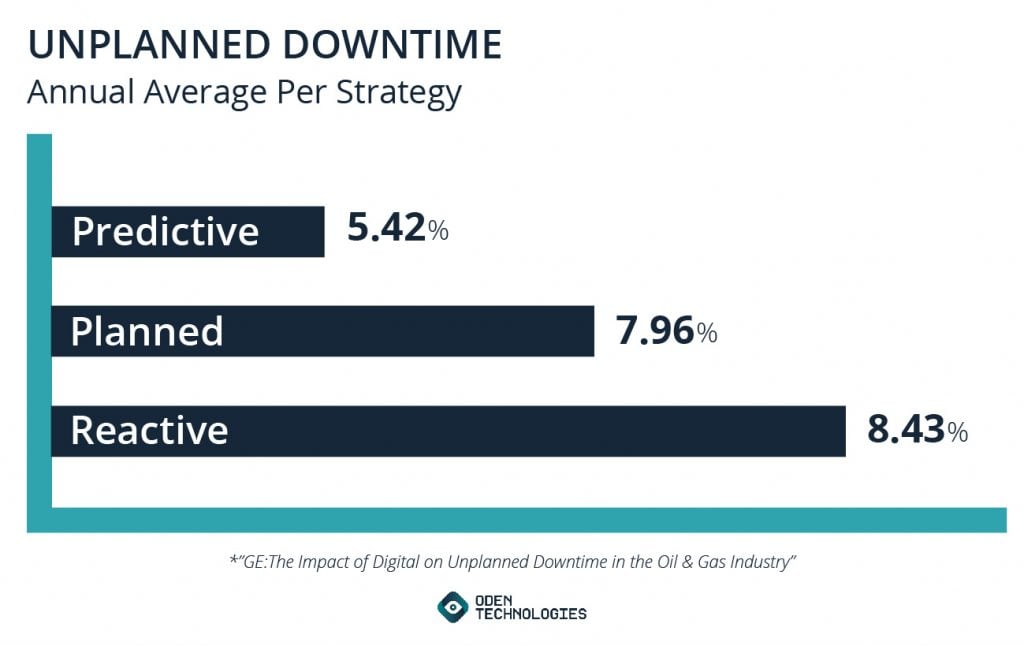
A GE Report on the oil and gas manufacture plant that only 24% of global operators who participated described their maintenance strategy equally "predictive," or an arroyo that is based on the efficient and effective drove and management of data and analytics. The most prevalent strategies used by the participants in the written report were the reactive arroyo or the planned arroyo.
In terms of the unplanned downtime associated with each of the three approaches:
• Reactive strategies averaged 8.43% in unplanned downtime annually.
• Planned strategies averaged 7.96% in unplanned downtime annually.
• Predictive strategies averaged 5.42% in unplanned reanimation annually.
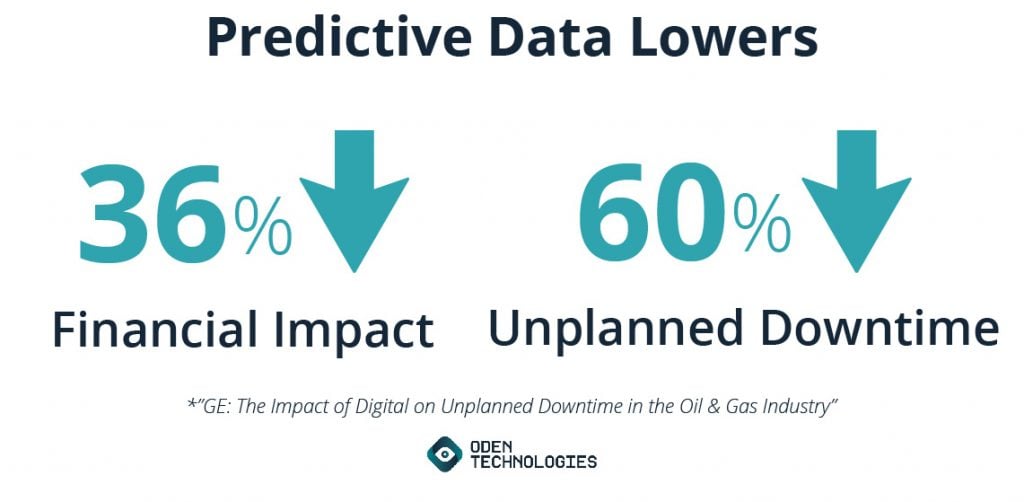
Compounded by the additional costs of repair, labor, transportation and equipment, the reactive and planned approaches pb to a hemorrhaging of revenue at simply shy of 60 million dollars annually. A predictive, data monitoring approach cuts those losses by about 40%. The numbers lend truth to the power of predictive information and analytics to significantly minimize the amount of reanimation a manufactory may meet.
Challenges Of Predictive Maintenance In Manufacturing
Information technology is of import to note that true "predictive maintenance" has its inherent challenges when implementing. A meaning investment of time is necessary to get together the data needed to predict very specific scenarios including reanimation in the manufacturing process.
A good dominion of thumb for predictive analytics is that you need x times the data of the scenario you are looking to predict. If you are looking to determine when a disquisitional piece of mechanism needs to be replaced, like a motor, that motor would need to fail x times in guild to assemble enough information to create a reliable prediction.
The solution to expediting the implementation of a predictive strategy and moving away from costly planned or reactive approaches is past combining the power of status-based monitoring of the manufactory floor, machine learning and predictive analytics.
Leveraging Machine Learning And Predictive Analytics
Status-based monitoring is when machine learning models await for a specific set of atmospheric condition that signal a machine failure may occur. The temperature and vibrations of key components on a motorcar are set based on optimal controls. These controls are continuously monitored, and when measurements on a machine are experiencing any deviations, such every bit a prolonged dip in temperature, or an increase in vibration, alerts are sent to notify factory personnel of a possible failure.
Predictive analytics are a tool that can be used to warning teams when loftier-productivity components, such as pumps, fans and motors, signify they might fail. Alerts are customizable to mill flooring conditions or any combination of metrics you may choose. If the condition-based monitoring registers a auto'south pressure has dropped v times over the course of ten minutes an alert is triggered to notify mill personnel that action is necessary. This alert not only pinpoints the deviation in optimal controls but empowers the factory floor operators to act decisively to foreclose unplanned reanimation.
The Perfect Reanimation Monitoring Platform
The perfect downtime monitoring platform combines real-time monitoring and pareto analysis with auto learning and predictive analytics. Real-time monitoring allows manufacturing companies to admission production data while it is happening. It allows you to see where a kink in the production line may exist occurring, why it happened, when information technology happened and much more. Pareto analysis is a technique used to assess and prioritize problems during product. By analyzing these, managers are able to focus their efforts on each private problem according to the strength of its touch on on daily operations.
Categorizing your reasons for production downtime into a Pareto Chart allows you to meet the largest causes of downtime in real-time. With visual representation of downtime, operators can determine what percentage and factors are causing reanimation and will be able to prioritize what to fix based on frequency and difficulty of the issues to solve. Machine learning & predictive analytics allow y'all to predict and preclude issues past alerting operators or engineers then they tin have corrective action immediately, ultimately costing them fifteen minutes versus five hours of unplanned downtime in the hereafter.
Downtime Calculation Applications In Many Industries
Downtime adding applications are useful in many manufacturing industries today. Oden Technologies helps a variety of industries limit unplanned downtime through the use of machine learning and predictive analytics including food and drink, wire and cable, and automotive.
Across the board, unplanned reanimation is plush. Failure of auto components or deviations from optimal settings not just lends to the product of scrap, only can also create unsafe working weather condition for factory floor personnel. The improper manufacture of resources, whether information technology is oil, or wire and cable will have a massive impact on the bottom line.
Oden's arroyo to condition-based monitoring and predictive analytics volition expedite the implementation of a predictive approach on your factory floor to drastically foreclose unplanned downtime, saving a tremendous amount of money in lost acquirement.
Get Oden's Help
Reanimation in manufacturing can exist a major headache during daily operations and inevitably results in a loss in acquirement. The less downtime, particularly unplanned, the meliorate.
Learn more than about using machine learning to eliminate unplanned downtime in manufacturing as well as predict and forbid production failures.

Source: https://oden.io/blog/downtime-in-manufacturing-the-true-cost/
Posted by: cainchicter1945.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Much Money Do Food Companies Lose During An Hour Of Downtime"
Post a Comment