| For an intuitive review of dilations, see the Refresher section Transformations: Dilations.
Now, let's expand that knowledge of dilations in relation to geometry.
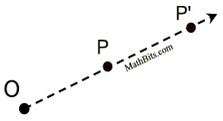
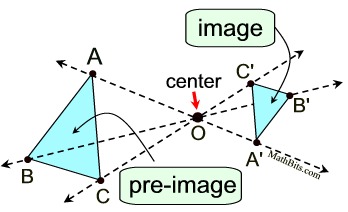
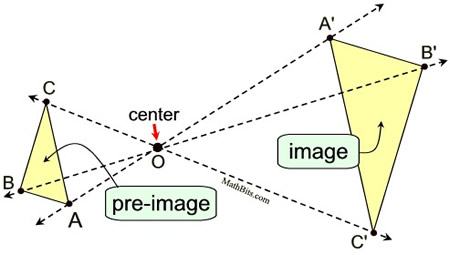
A dilation is a transformation that produces an image that is the same shape as the original, but is a different size. The description of a dilation includes the scale factor (constant of dilation) and the center of the dilation. The center of a dilation is a fixed point in the plane about which all points are expanded or contracted. The center is the only invariant (not changing) point under a dilation (k ≠1), and may be located inside, outside, or on a figure. Note: A dilation is NOT referred to as a rigid transformation (or isometry) because the image is NOT necessarily the same size as the pre-image (and rigid transformations preserve length). Referring to the diagram below:
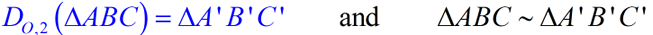
The dilation (centered at O with a scale factor of 2) of ΔABC = ΔA'B'C' making ΔABC ∼ ΔA'B'C' .
This could also be written 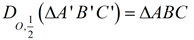 if you consider ΔABC to be the image. if you consider ΔABC to be the image.
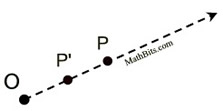
| | 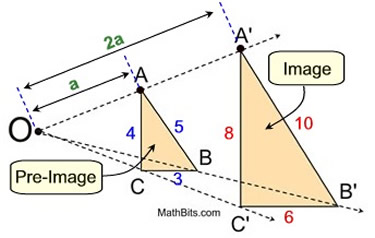 Dilations create similar figures! Dilations create similar figures! | In this dilation, of scale factor 2 mapping ΔABC to ΔA'B'C', the distances from O to the vertices of ΔA'B'C' are twice the distances from O to ΔABC. After a dilation, the pre-image and image have the same shape but not the same size. Sides: In a dilation, the sides of the pre-image and the corresponding sides of the image are proportional.
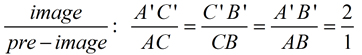 | Properties preserved under a dilation from the pre-image to the image.
1. angle measures (remain the same)
2. parallelism (parallel lines remain parallel)
3. collinearity (points remain on the same lines)
4. orientation (lettering order remains the same)
----------------------------------------------------------
5. distance is NOT preserved (lengths of segments are NOT the same in all cases except a scale factor of 1).
A dilation is NOT a rigid transformation (isometry). | Scale Factor, k: • If k > 1, enlargement.
• If 0 < k < 1, reduction.
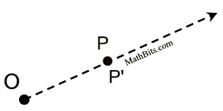
• If k = 1, congruence. If k < 0, the image will be placed on the opposite side of the center and rotated 180º. Since sides of length 0 do not exist, and division by 0 is not allowed, scale factors are never listed as zero (k ≠0). |  ΔD'E'F' is the image of ΔDEF (dilation center O, scale factor ½). ΔD'E'F' is the image of ΔDEF (dilation center O, scale factor ½). | Distances from the center:
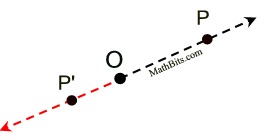
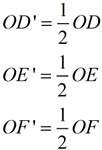 | 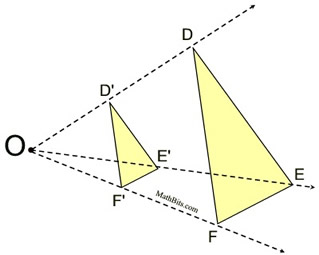 | |  | A dilation is a transformation, DO,k , with center O and a scale factor of k that is not zero, that maps O to itself and any other point P to P'. | | The center O is a fixed point, P' is the image of P, points O, P and P' are collinear, and 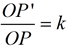 . . | What happens when scale factor k is a negative value?
If the value of scale factor k is negative, the dilation takes place in the opposite direction from the center of dilation on the same straight line containing the center and the pre-image point. (This "opposite" placement may be referred to as being a " directed segment " since it has the property of being located in a specific "direction" in relation to the center of dilation.) Case 4: -1 < k < 0
Directed Segments - Reduction
Center of dilation O,
scale factor of -½.
 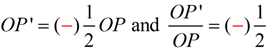
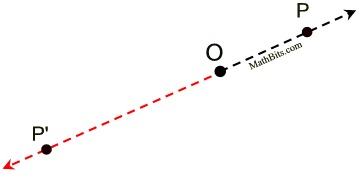
(The negative symbol indicates "direction", not negative length.) | Case 5: k < -1
Directed Segments - Enlargement
Center of dilation O,
scale factor of -2.
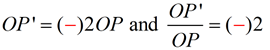
| | Note: Consider that when the absolute value of the scale factor is greater than 1 , the image will be larger than
the pre-image. (When k < -1, the image is larger, with a 180º rotation. The negative symbol indicates direction.)
When the absolute value of the scale factor is between 0 and 1, the image will be smaller than the pre-image.
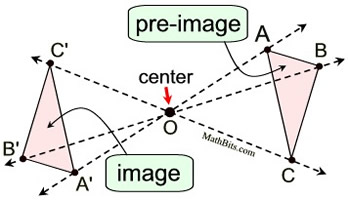
(When -1< k < 0, the image is smaller, with a 180º rotation.) | Let's see how a negative dilation affects a triangle:
Notice that the "image" triangles are on the opposite side of the center of the dilation (vertices are on opposite side of O from the preimage). Also notice that the triangles have been rotated 180º . Did you notice the connection between negative dilations and rotations? When k = -1, the triangles are congruent and the negative one scale factor produces the exact same result as a rotation of 180º centered at O. We can write: 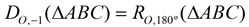 . . This direct connection between dilations and rotations does NOT extend to dilations whose scale factors do NOT equal -1, such as the dilations of k = -½ and k = -2. These dilations do not preserve length, and rotations must preserve length. We can, however, express these dilations as a composition of transformations involving a rotation. For example, when k = -2 , we can also describe that transformation as a dilation of scale factor +2 combined with a rotation of 180º (both centered at O). We can write: 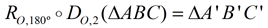 
Dilations on Coordinate Axis:  Dilation with Center at Origin, (0,0): Dilation with Center at Origin, (0,0):
The most popular dilation on a coordinate axis is a dilation centered at the origin. The majority of the dilation questions in Geometry are centered at the origin. Note that both the x and y coordinates are multiplied by the SAME value, k. Formula: Center at Origin:
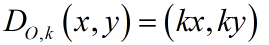
O = center of dilation at (0,0);k = scale factor  | Given ΔDEF with center of dilation the origin (0,0) and scale factor of 2, plot ΔD'E'F'.
D(0,4), E(1,-2), and F(-4,2)
As shown in the formula above, multiply each x and y coordinate value by the scale factor of 2 to find the new coordinates. D (0,4) becomes D' (0,8)
E (1,-2) becomes E' (2,-4)
F (-4,2) becomes F' (-8,4) Let the center (0,0) be labeled O: Distance from center:
OF' = 2OF
OE' = 2OE
OD' = 2OD | Length of Δ sides:
F'D' = 2FD
D'E' = 2DE
F'E' = 2FE | | 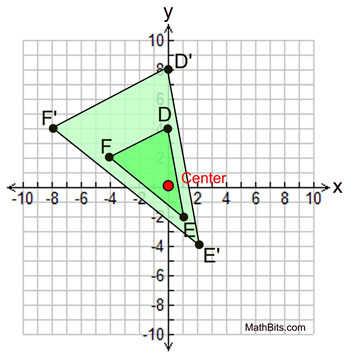 |  Dilation with Center NOT at Origin: Dilation with Center NOT at Origin:
A dilation on a coordinate axis where the center is NOT the origin can be accomplished by observing the vertical and horizontal distances of each vertex from the center of dilation. In essence, we will be looking at the "slope" of each line (segment) involved.  | Part 1: Given point C (-2,-1), center of dilation of (-4,-9), and scale factor of 2, find C'. By observation, point C is 8 vertical units above the center of dilation. Under a scale factor of 2, point C' needs to be 16 vertical units from the center. Also, point C is 2 horizontal units right of the center of dilation. Point C' needs to be 4 horizontal units right of the center. Starting at the center of dilation (-4,-9), move 16 units up and 4 units to the right to find C' at (0,7). NOTE: We are maintaining the slope of the line passing through the center, point C, and point C'. | 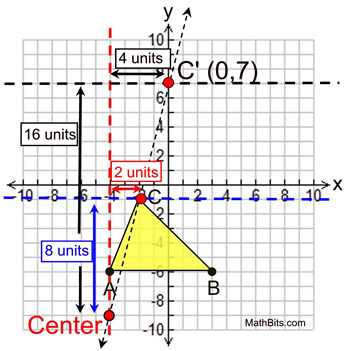 | |
Part 2: Plot the dilation of ΔABC by a scale factor of 2 with a center of dilation at (-4,-9).
A(-4,-6), B(3,-6), and C(-2,-1) By observing vertical and horizontal distances from the center of dilation, as seen in Part 1, you can find the remaining two coordinates of the dilated triangle. A'(-4,-3), B'(10,-3), C'(0,7) | 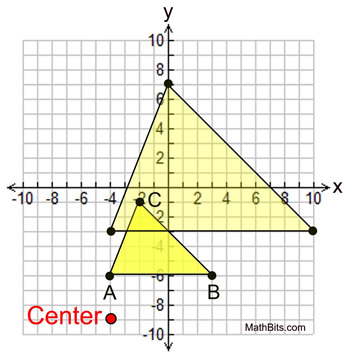 |  The counting of vertical and horizontal distances shown above is a simple and easy way to find the coordinates for a dilation not centered at the origin. FYI: Another Method
A dilation not centered at the origin, can also be thought of as a series of translations, and expressed as a formula. Translate the center of the dilation to the origin, apply the dilation factor as shown in the "center at origin" formula, then translate the center back (undo the translation). • First translate the center of the dilation so the origin becomes the center.
Subtracting the coordinate values of the center of dilation will move the center to the origin.
Given center of dilation at (a,b), translate the center to (0,0): (x - a , y - b ). • Then apply the dilation factor, k: ( k (x -a), k (y -b)) • And translate back: (k(x - a) + a, k(y - b) + b ) Formula: Center Not at Origin:
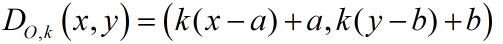
O = center of dilation at (a,b); k = scale factor

Write a coordinate rule to find the vertices of a dilation with center (4,-2)
and scale factor of 3. Let (x,y) be a vertex of the figure.
Translate so the origin becomes center of the dilation (left 4 and up 2): (x - 4, y + 2).
Apply the dilation formula when centered at origin: (3(x - 4), 3(y + 2)) = (3x - 12, 3y + 6)
Translate back (right 4 and down 2): (3x - 12 + 4, 3y + 6 - 2) = (3x - 8, 3y + 4) Rule: (x,y) → (3x - 8, 3y + 4) For example, under this dilation, the point (5,6) becomes (3(5)-8, 3(6)+4) which is (7,22). 
NOTE: The re-posting of materials (in part or whole) from this site to the Internet is copyright violation
and is not considered "fair use" for educators. Please read the "Terms of Use". |


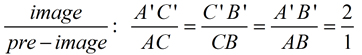
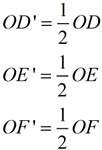

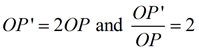

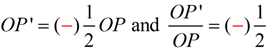

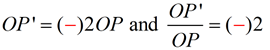
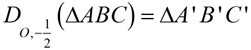



0 Response to "how to find the center of dilation"
Post a Comment